German Language Levels
Do you find it difficult to understand the different levels of German language proficiency? Are you overwhelmed and confused by terms like A1, B2 and C1?
Don’t be afraid!
In this comprehensive guide, we will look at the various German language levels and give you a clear understanding of what each level covers.
Whether you are brushing up on your skills or starting from scratch as a beginner, this article is here to help you navigate the complexities of learning German.
So grab a cup of coffee and get ready to dive into the German world 🙂
Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR)
The Common European Framework of Reference for Languages, or CEFR, is a standardized system for measuring and assessing language proficiency across Europe. It was developed by the Council of Europe to promote consistency and transparency in language learning and teaching. The framework is divided into six levels, from A1 (beginner) to C2 (advanced), with each level focusing on different aspects of language such as vocabulary, grammar, reading comprehension, writing skills, etc.
One of the main benefits of using the CEFR is that it provides a common language for describing language ability across national borders. This means that regardless of whether you are learning German in Germany, France or Spain, your language level can be easily understood and recognized by employers or institutions that require proof of your skills. In addition to this practical advantage, the framework also encourages students to set achievable goals based on their individual needs and interests. By setting realistic goals at each level, you can monitor your progress more effectively and feel confident in your skills as you progress from beginner to advanced!
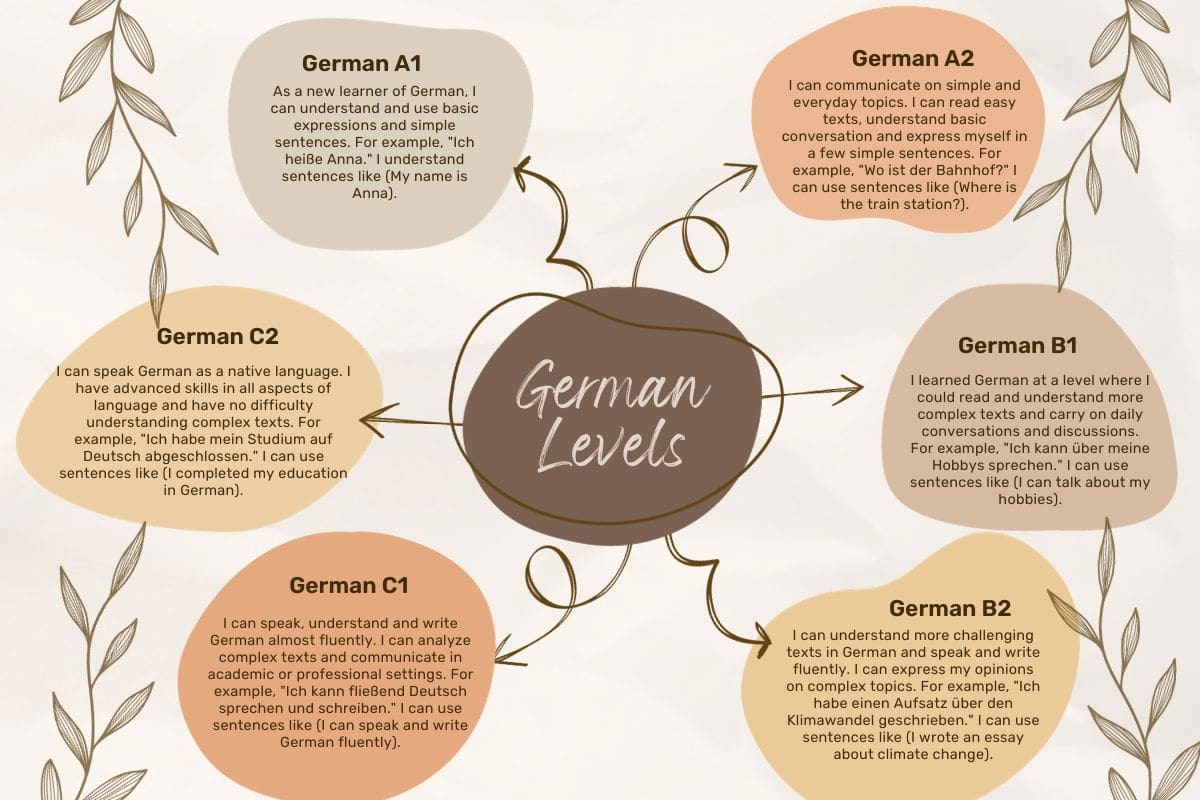
A1: Beginner Level
Learning a new language can be an exciting but daunting experience, especially when it comes to understanding different levels of proficiency.
In German A1 beginner level, students are introduced to basic concepts such as simple expressions and vocabulary that enable them to have everyday conversations with native speakers.
Some examples of topics covered at this level include personal information such as name and nationality, expressing likes and dislikes, ordering food in a restaurant or café, asking for directions, among others.
For those who want to start learning German from scratch or brush up on basic skills, A1 is usually the best starting point. Although students may initially feel overwhelmed by the sheer amount of new information they are expected to assimilate, staying motivated and consistent with their study patterns will help them progress quickly through the various stages at this level.
Once you have mastered beginner level A1 German skills such as pronunciation and sentence structure, it becomes much easier to move on to more complex levels such as B2 or C1.
A2: Beginner Level
A2: Beginner Level is the second level in the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) and corresponds to basic proficiency in German.
At this level, students can understand sentences and frequently used expressions related to areas of close personal interest, such as simple conversations about family or shopping. They can also communicate in simple and routine tasks that require direct exchange of information on familiar topics.
For students who are just beginning their German learning journey, reaching A2: Beginner Level may seem like an insurmountable task. However, with constant practice and immersion in the language through reading and listening exercises, it is even possible to go beyond this point. This article aims to alleviate fears by providing a clear understanding of how much to expect of themselves over time to help new learners gain confidence as they strive to master basic usage skills!
B1: Intermediate Level
Level B1 marks an important milestone in your language learning journey. As an intermediate speaker, you will be able to hold conversations on familiar topics and express your thoughts and ideas with relative ease. You may still struggle with more complex grammatical structures and idiomatic expressions, but with practice your skills will continue to improve.
At this level, you can begin to engage more deeply with German culture by reading books or watching movies without subtitles. You may also feel comfortable traveling to German-speaking countries and interacting confidently with locals. With continued dedication and study, moving on to higher levels of proficiency becomes a real possibility.
Overall, achieving level B1 is something to be proud of! It represents a significant achievement in learning German and opens up many new opportunities for personal development and growth. So keep practicing, immerse yourself in the language as much as possible and don’t forget to celebrate your progress along the way!
B2: Upper-Intermediate Level
B2 is the third highest level of German language proficiency. It represents the upper-intermediate level of fluency, where students can communicate effectively on a wide range of topics and handle most everyday situations with ease. At this stage, students should have a good grasp of grammar and syntax and should be able to produce longer and more complex sentences without too much difficulty.
To reach level B2, students need to be able to understand and respond appropriately to oral and written material from a variety of sources, such as news articles, debates or speeches. They should also be able to express their opinions clearly on abstract or cultural topics, often using more idiomatic expressions typical of the German language.
Also, at level B2, students will continue to perfect their reading comprehension skills, which enable them to read novels or literature without feeling overwhelmed. Overall it takes effort, but reaching level B1 can bring great rewards, as their learning curve will no longer feel like a steep hill, but rather like intermediate steps.
C1: Advanced Level
C1 is considered an advanced level of German proficiency, often referred to as the “Effective Operational Proficiency” stage. Students who reach this level have a deep understanding and appreciation of the language that enables them to communicate effectively in both professional and social settings. At this point, students are expected to be able to produce complex texts on a variety of topics with ease and to be able to understand abstract or academic writing.
An important advantage of achieving proficiency at C1 level is that you can use your language skills for a wide variety of purposes. For example, learners at this level will find it relatively easy to read newspapers and news articles without constantly needing the help of a dictionary. They can also communicate comfortably with native speakers without feeling lost or left out during conversations.
Overall, achieving fluency at C1 level requires time and dedication for students who are willing to put sustained effort into their studies. It requires perseverance but also patience, recognizing progress where it exists while remaining humble when challenges are encountered along the way. With practice comes success – so go ahead and take your first step towards learning German today!
C2: Adequate Level
At proficiency level C2, a learner has reached a level of fluency in German close to that of a native speaker. They can effortlessly understand and communicate complex ideas with great accuracy in a variety of social and professional situations. At this stage, students will have mastered all grammar rules, including complex sentence structures and advanced vocabulary.
The degree of precision expected at this level is high, with little or no grammatical errors when speaking or writing in German. Students who reach C2 proficiency can usually use idiomatic expressions and regional variations with confidence and mastery. They may also have an advanced knowledge of German culture, history and literature, enabling them to give stimulating speeches on a variety of topics related to Germany.
Speakers with C2 proficiency can be compared to bilingual individuals in terms of their mastery of the grammatical rules of both languages. It takes a significant investment of time (and often concentration) in language learning for a non-native German speaker to reach this level of fluency, but it pays off by providing access to more extensive learning opportunities, such as studying abroad or working in Germany’s professional fields.
How to determine your German language level
Determining your German language level can be a daunting task, but it is an important step towards achieving fluency. The first thing you need to determine is your purpose for learning the language – whether for personal or professional reasons. Once you have identified your goals, take an online placement test to assess your current level of proficiency in each of the four components of the language (reading, writing, speaking and listening).
You can measure your current level by taking the 100-question Online German Level test we have prepared for you.
The Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) sets six levels of proficiency that are recognized as standard worldwide. These range from A1 (beginner) to C2 (advanced). It is important to note that each level has specific criteria based on what you can say and understand in terms of grammar points, vocabulary and syntactic structures.
Other factors that can influence determining one’s level include exposure to the German-speaking environment, such as immersion programs or living with native speakers; self-study through textbooks or taking formal lessons in language institutions – all these aspects will contribute positively to benchmarking one’s abilities against the CEFR standards and thus provide confidence when communicating in German in various situations, including job interviews, personal travel, etc.
What are the requirements for each German language level?
To begin with, it is important to note that German language proficiency levels are divided into six categories: A1, A2, B1, B2, C1 and C2. Each level has specific requirements that must be met to demonstrate proficiency. For example, at A1 level, individuals should be able to express themselves in basic conversations using common phrases and vocabulary related to common situations such as shopping or traveling.
As learners progress through levels A2-B2, they will need a deeper understanding of grammar rules and more knowledge of idiomatic expressions. Higher levels (C1-C2) require an even more developed vocabulary as well as strong comprehension skills that can determine whether a speaker is fluent in German. In addition, these higher levels may include complex areas such as science and technology or political and legal issues, depending on the students’ interest in these areas.
Overall, whether you are learning German for personal reasons or for professional advancement, understanding the different levels of proficiency can help you monitor your progress and ensure that you meet certain standards at each stage of your journey. Remember; practice constantly, no matter how challenging it may feel at first, and take tests/exams regularly if you are fully motivated to get full certification that proves its usefulness in the real world while traveling, especially with the endless opportunities that come your way in the European and Middle Eastern regions where it feels almost mandatory!
How to prepare for German proficiency tests
Preparing for a German language proficiency test can seem daunting, but with the right approach you can successfully pass any test. First of all, it is very important to familiarize yourself with the specific requirements of the exam you are taking. Learn about its format, timing and scoring system. This information will help you structure your study plan accordingly.
Once you understand what is expected during the exam, it is time to assess your current skill level in German. Take practice tests or review past exams to identify areas for improvement. Focus on strengthening your weaknesses while maintaining your strengths.
Finally, immerse yourself in German as much as possible by using resources such as textbooks with exercises and audio recordings to practice listening comprehension, or by finding online tools such as language exchange sites where people chat in their own language. All of these tips combined will ensure that you are effectively prepared for any German proficiency test!
Tips to improve your German language skills
Improving your German language skills can seem daunting at first, especially if you are new to the language. However, there are a few tips that can help you improve your learning experience. One effective way is to immerse yourself in the language by watching German movies and TV shows, listening to German podcasts or audiobooks, and reading German texts such as news articles or books. It is also important to regularly practice speaking with native German speakers or other students.
Another useful tip is to establish a structured study routine that includes grammar exercises, vocabulary building activities and regular assessment of your progress. You can find many resources online or in language schools that offer courses suitable for different skill levels.
Overall, improving your German proficiency requires commitment and dedication, but with consistent effort over time you will see significant progress!
German language resources and tools
If you are looking for resources and tools to help you learn German, there are many options available. Some popular options include language learning apps like Duolingo or Babbel, online courses like those offered by Rosetta Stone or the Goethe Institut, and textbooks like the “Deutsch als Fremdsprache” series. There are also many websites offering free language exercises and grammar explanations, such as Lingoda or The German Project.
Another valuable resource for German learners are immersion programs. These programs can be found in Germany or in other countries with large German-speaking populations, such as Austria or Switzerland. Immersion programs offer students the opportunity to practice conversational skills through real-life interactions and experiences, while deepening their understanding of German culture and traditions.
Overall, when it comes to learning German, it is important to find the best fit for your individual needs. Whether it’s a combination of various resources or a specific tool that appeals to you the most – persistence and dedication will ultimately pay off as you become more confident in your ability to communicate in this beautiful language!
The importance of vocabulary in learning German
One of the most important aspects of learning German is building a strong vocabulary. The ability to understand and use new words can greatly increase your language proficiency and help you communicate better with native German speakers. Understanding basic vocabulary is especially important for beginners, as it lays the foundation for more advanced concepts.
Furthermore, having a large vocabulary enables language learners to understand phrases and expressions that do not have direct translations in their own language. This helps students to fully grasp the nuances of the German language and culture, while also enabling them to accurately convey their thoughts and ideas.
Mastering new vocabulary can take time, but constant practice through reading, writing, speaking and listening exercises will greatly speed up the process. Students who prioritize vocabulary acquisition alongside knowledge of grammar rules and sentence structure will find that they take important steps towards mastering this beautiful language in no time!
Grammar rules and structures in German
When it comes to understanding German, one must first familiarize oneself with its grammatical rules and structures. Unlike English, which has a relatively simple structure, German is known for its complex system of cases, conjugations and inflections. To master this language, one must be willing to invest time and effort in understanding these nuances.
One of the most important aspects of German grammar is the use of cases. There are four different cases in the language: nominative (subject), accusative (direct object), dative (indirect object) and genitive (possessive). Each case changes the form of articles, adjectives and/or pronouns depending on their function in the sentence. Also, nouns are declined according to gender: masculine, feminine or neuter.
In addition, verb conjugation plays an important role in German sentence construction. Verbs must agree with their subjects in both tense and person. For example, “Ich liebe” means “I love”, while “Wir lieben” means “We love”. Moreover, strong verbs have irregular forms that do not follow a pattern, making them essential components for students aiming beyond basic conversational proficiency levels.
Understanding these basic aspects will enable you to grasp properly formed sentences while improving your ability to understand written or spoken input, and will give you the confidence to easily interact with native German speakers at every stage as you progress towards fluency level skills!
The role of listening and speaking in German language proficiency
When it comes to learning German, one of the most important skills you need to develop is listening and speaking. These two skills are essential for effective communication in any language, including German. Listening helps you understand the pronunciation, accents and word usage of native German speakers. It also allows you to catch nuances in sentence structure and intonation patterns – all vital components that help improve your comprehension.
Speaking gives you the opportunity to apply what you have learned. Getting the pronunciation right can be challenging at the beginning as it can take a lot of effort (especially with umlauts). However, when mastered correctly, this skill set will give students plenty of confidence when speaking to others in real-life scenarios, from casual small talk to formal business meetings.
In summary, both listening and speaking are critical skills needed when trying to understand or communicate effectively using the German language. Therefore, investing valuable study time to practice in these specific areas to increase proficiency levels will benefit anyone seeking a higher proficiency level in German!
Reading and writing in German: Tips and strategies
When it comes to reading and writing in German, there are several tips and strategies that can greatly improve your language skills. One of the most effective ways to improve your reading skills is to regularly expose yourself to authentic German texts such as newspapers, magazines, books or blogs. Start with shorter articles and gradually work your way up to longer pieces covering a variety of topics. This practice will help you improve your vocabulary and grammar knowledge while also improving comprehension.
Similarly, practicing writing in German can be very useful for language learners. Whether it is keeping a diary of daily activities or communicating with native German speakers via email, regular writing exercises will help to develop more natural sentence structures and grammar usage over time. In addition, getting feedback from a teacher or online resource can help identify areas for improvement and provide opportunities for further learning.
Overall, consistent use of these tips and strategies is the key to progressing through the different proficiency levels in German. With patience, dedication and the right tools, such as Duolingo or Rosetta Stone courses, anyone can become proficient in German!
Common mistakes to avoid when learning German
Learning a new language can be difficult and German is no exception. However, there are some common mistakes students make that you should avoid. First, remember to practice regularly. Consistency is key when it comes to mastering any skill – make time to study and practice every day, even if it’s for a short period of time.
Another mistake is not immersing yourself enough in the language. Don’t rely solely on textbooks and lectures to learn German; try listening to podcasts or watching German TV shows to familiarize yourself with the pronunciation and context of different words and expressions. Finally, don’t be afraid to ask questions or make mistakes! Learning is a process, so accept your mistakes as opportunities for growth and correction from others who may have more experience than you.
By avoiding these common pitfalls when learning German, you will be able to move much faster towards achieving fluency in this beautiful language!
Overcoming difficulties in learning German
Learning German can be a challenging journey, but it is definitely worth the effort. One of the biggest challenges for language learners is understanding and navigating through the various levels of proficiency. The Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) divides language proficiency into six levels, from A1 (beginner) to C2 (advanced).
To meet this challenge, language learners can make use of a variety of resources such as textbooks, online courses and private lessons to master each level before moving on to the next. Also, regular practice with native German speakers can help build confidence in communicating using conversational German.
Another challenge when learning German is mastering the pronunciation and grammar rules specific to the language. However, practice through consistent listening exercises and speaking opportunities will help students achieve fluency faster.
In conclusion, overcoming the challenges in learning German requires dedication and active engagement with the different learning strategies and tools available. With time, patience and practice, every student can develop their skills to advanced stages, become proficient in literacy and even communicate spontaneously with Germans!
Benefits of learning German
Learning German can be a highly useful skill for both personal and professional development. For beginners, it offers opportunities to communicate with more than 100 million people worldwide who speak the language, including countries such as Germany, Austria, Switzerland and Luxembourg. Moreover, acquiring knowledge of German can significantly improve career prospects. With a rapidly growing economy and job opportunities in numerous sectors such as automotive engineering and pharmaceuticals, proficiency in German can boost job prospects globally.
In addition to expanding communication channels or improving employability skills, there are also various cognitive benefits of learning an additional language. Research shows that learning a second language can help increase mental agility while improving problem-solving skills. Additionally, gaining experience in multiple cultures encourages acceptance of diversity among students, while enabling them to travel comfortably around the world without language barriers. All these advantages make learning German not only enriching but also practical for anyone seeking personal or professional development related to linguistic proficiency!
Your next steps to master the German language
Now that you understand the different levels of German language proficiency, it is time to take action and improve your skills. The first step is to assess your current level by taking a placement test or getting feedback from a qualified teacher. Once you know where you stand, set achievable goals according to the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR).
To move to the next level, immerse yourself in the language as much as possible. This can be done by reading German newspapers and books, watching subtitled TV shows or movies, listening to German podcasts or music, and practicing speaking with native speakers.
Finally, consider enrolling in a language course or finding a tutor who can provide personalized guidance and support. Remember that learning a new language takes time and patience, but with dedication and practice, you can master German!